About Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)
- 5 minsAbout Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)
What is Distributed Ledger Technology?
A distributed ledger is a type of data structure which resides across multiple computer devices, generally spread across locations or regions.
Distributed Ledger Technology includes blockchain technologies and smart contracts. While distributed ledgers existed prior to Bitcoin including time stamping of transactions, Peer-to-Peer(P2P) networks, cryptography, and shared computational power, along with a new consensus algorithm.
In summary, distributed ledger technology generally consists of three basic components:
-
A
data modelthat captures the current state of the ledger (a time stamped series of transactions cryptographically secured) -
A
language of transactionsthat changes the ledger state[Smart Contracts/Chain code] -
A
protocalused to build consensus among participants around which transactions will be accepted, and in what order, by the ledger
Smart contracts are simply computer programs that execute predefined actions when certain conditions within the system are met.
Consensus refers to a system of ensuring that parties agree to a certain state of the system as the true state.
Difference between Distributed Ledger & Blockchain
Blockchain is a specific form or subset of distributed ledger technologies, which constructs a chronological chain of blocks, hence the name block chain
A block refers to a set of transactions that are bundled together and added to the chain at the same time. in the bitcoin blockchain, the miner nodes bundle unconfirmed and valid transactions into a block. Each block contains a given number of transactions. In the bitcoin network, miners must solve a cryptographic challenge to propose the next block. This process is known as ‘proof of work’, and requires significant computing power.
Transactions The record of an event, cryptographically secured with a digital signature, that is verified, ordered, and bundled together into blocks, form the transactions in the blockchain.
Cryptography has a key role to play both in security, as well as in the immutability of the transactions recorded on blockchains. Cryptography is the study of the techniques used to allow secure communication between different parties and to ensure the authenticity and immutability of the data being communicated. For blockchain technologies, cryptography is used to prove that a transaction was created by the right person. It is also used to link transactions into a block in a tamper-proof way, as well as create the links between blocks, to form a blockchain.
Timestamping is another key feature of blockchain technology. Each block is timestamped, with each new block referring to the previous block. Combined with cryptographic hashes, this timestamped chain of blocks provides an immutable record of all transactions in the network, from the very first block.
A block commonly consist of four peices of metadata:
- The reference to the previous block
- The proof of work, also known as a nonce.
- The timestamp
- The Merkle tree root for the transactions included in this block.
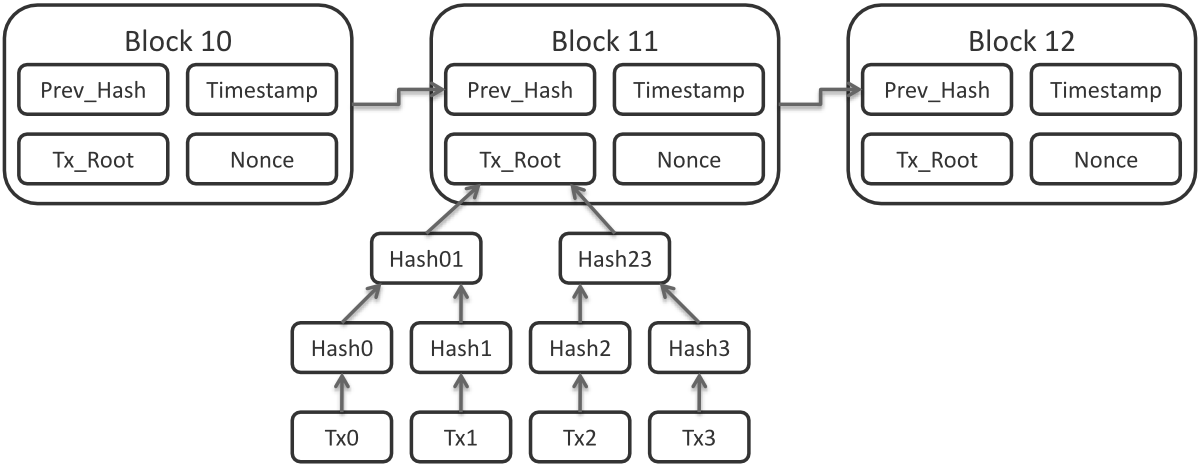
Merkle trees are used to summarize all the transactions in a block, producing an overall digital fingerprint of the entire set of transactions, providing a very efficient process to verify whether a transaction is included in a block.
Consensus is a process whereby the computeres that are part of the network synchronized the data on the blockchain. Consensus in the network refers to the process of achieving agreement among the network participants as to the correct state of data on the system. Consensus leads to all nodes sharing the exact same data. A consensus algorithm, hence, does tow things: it ensures that the data on the ledger is the same for all the nodes in the network, and, in turn, prevents malicious actors from manipulating the data. The consensus algorithm varies with different blockchain implementations.
There are a number of consensus mechanisms or algorithms
- Proof of Work(PoW)
- Proof of Stake(PoS)
- Proof of Elapsed Time(PoET)
- Simplified Byzantine Fault Tolerance(SBFT)
- Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance(PBFT)
- Proof of Authority(PoA)
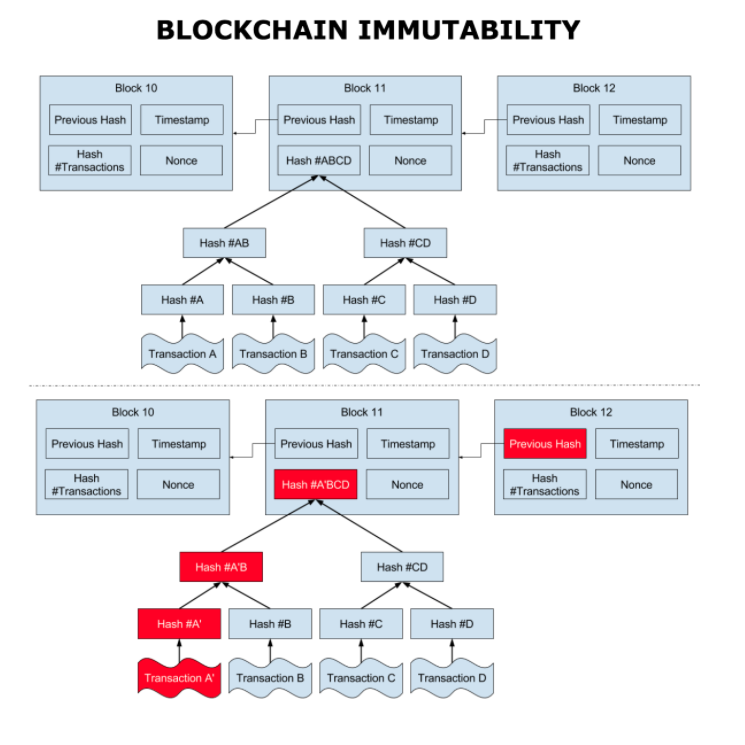
The Immutability of the Data
The immutability of the data which sits on the blockchain is perhaps the mos tpowerful and convincing reason to deploy blockchain-based solutions for a variety of socio-economic processes which are currently recorded on centralized servers.
This immutability, or unchanging over time feature makes the blockchain useful for accounting, financial transactions, identity management, and asset ownership, management and transfer, just to name a few examples.
once a transaction is written onto the blockchain, no one can change it, or, at least, it would be extremly difficult to change it,
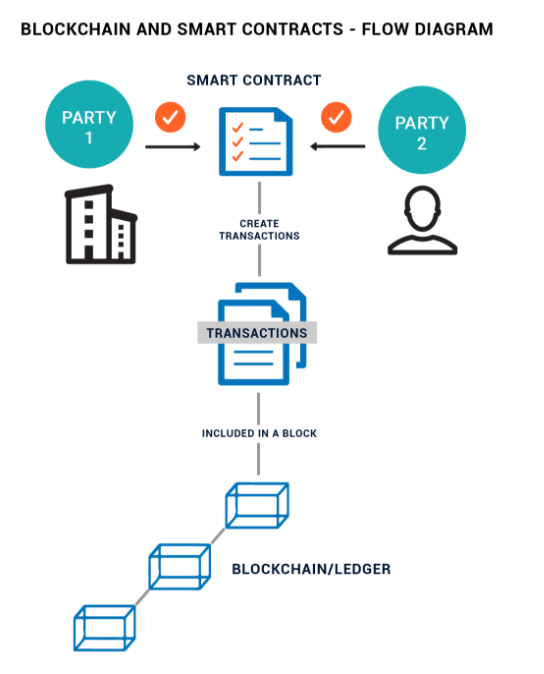
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are simply computer programs that execute predefined action when certain conditions within the system are met. Smart contracts provide the language of transactions that allow the ledger state to be modified. They can facilitate the exchange and transfer of anything of value.
Types of Blockchain
- Permissionless Blockchain(like bitcoin)
- Permissioned Blockchain(like the different Hyperledger blockchain frameworks).
A permissionless blockchain is also known as a public blockchain, because anyone can join the network.
A permissioned blockchain, or private blockchain, requires pre-verification of the participating parties within the network, and these parties are usually known to each other.
Recap
* The data model for a DLT (Distributed Ledger Technology) is a version of Blockchain
. Transactions make a block
. Block has the reference to the previous block, The proof of work, also known as a nonce (consensus parameter), The timestamp, The Merkle tree root for the transactions included in this block.
. A cryptographically secured chain of blocks is blockchain
* A protocol used to build consensus among participants around which transactions will be accepted, and in what order, by the ledger is called consensus. Various consensus algorithms are available and you choose what's best for your solution based on certain parameters defined above.
* Smart contracts - A language of transactions that changes the ledger state
Reference
- https://medium.com/swlh/hyperledger-chapter-1-foundation-7ad5bd94d452